Since a few releases ago, Oracle has introduced native connectors that link Oracle Analytics to Oracle EPM Applications. This integration enables planning data from Oracle EPM Cloud to be seamlessly retrieved into Oracle Analytics for reporting and analysis.
However, this initial step only scratches the surface of the EPM/Essbase ecosystem. Several additional capabilities are needed to fully leverage these data sources, including:
- Support for EPM Cloud/Essbase data sources in the Semantic Modeler: This feature is not yet available but is expected in the January 2025 release of Oracle Analytics Cloud.
- Direct import of Substitution Variables with data is not currently supported. However, REST API provides a way to retrieve all substitution variables.
- Selection Steps, a functionality familiar from "classic" Oracle Analytics (Dashboards and Answers), allows users to select specific hierarchy members and display only their descendants based on hierarchical or similar relationships (e.g., leaves of a hierarchy).
This article focuses on retrieving Substitution Variables using the REST API and integrating them into Oracle Analytics.
Understanding the Challenge: What Are Substitution Variables?
Substitution variables are placeholders defined within the Oracle EPM Cloud or Essbase data sources. They represent specific members that change regularly, such as versions or periods. Bringing these substitution variables into Oracle Analytics ensures consistency in reporting and analysis, allowing dynamic filtering and parameterization aligned with the source system.
Unfortunately, substitution variables cannot be imported directly with the data via native connectors. The workaround is to use the Oracle EPM Cloud REST API to extract these variables and incorporate them into Oracle Analytics.
Overview of the Workflow
To leverage substitution variables in Oracle Analytics, the workflow involves:
- Creating a new REST API connection to Oracle EPM Cloud.
- Building a dataset in Oracle Analytics that retrieves substitution variables via this REST API connection.
- Using the substitution variables dataset to create parameters within workbooks.
- Binding these parameters to filters or using them independently in analyses (e.g., expression filters, calculations).
Initial Workbook Setup
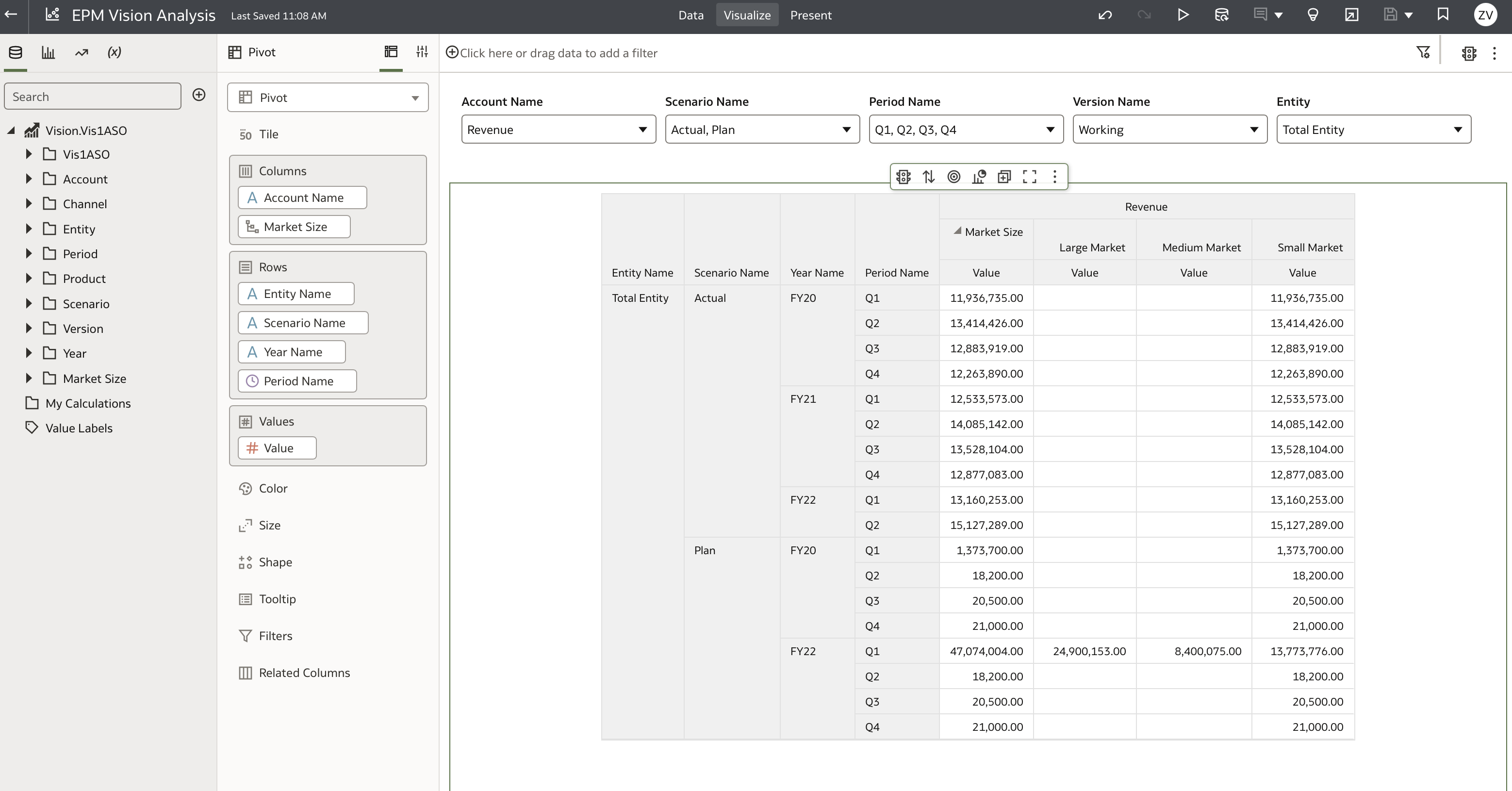
Our starting point is a workbook with a dataset named Vision.Vis1ASO. This dataset uses a direct native connection to the Oracle EPM Planning application and cube.
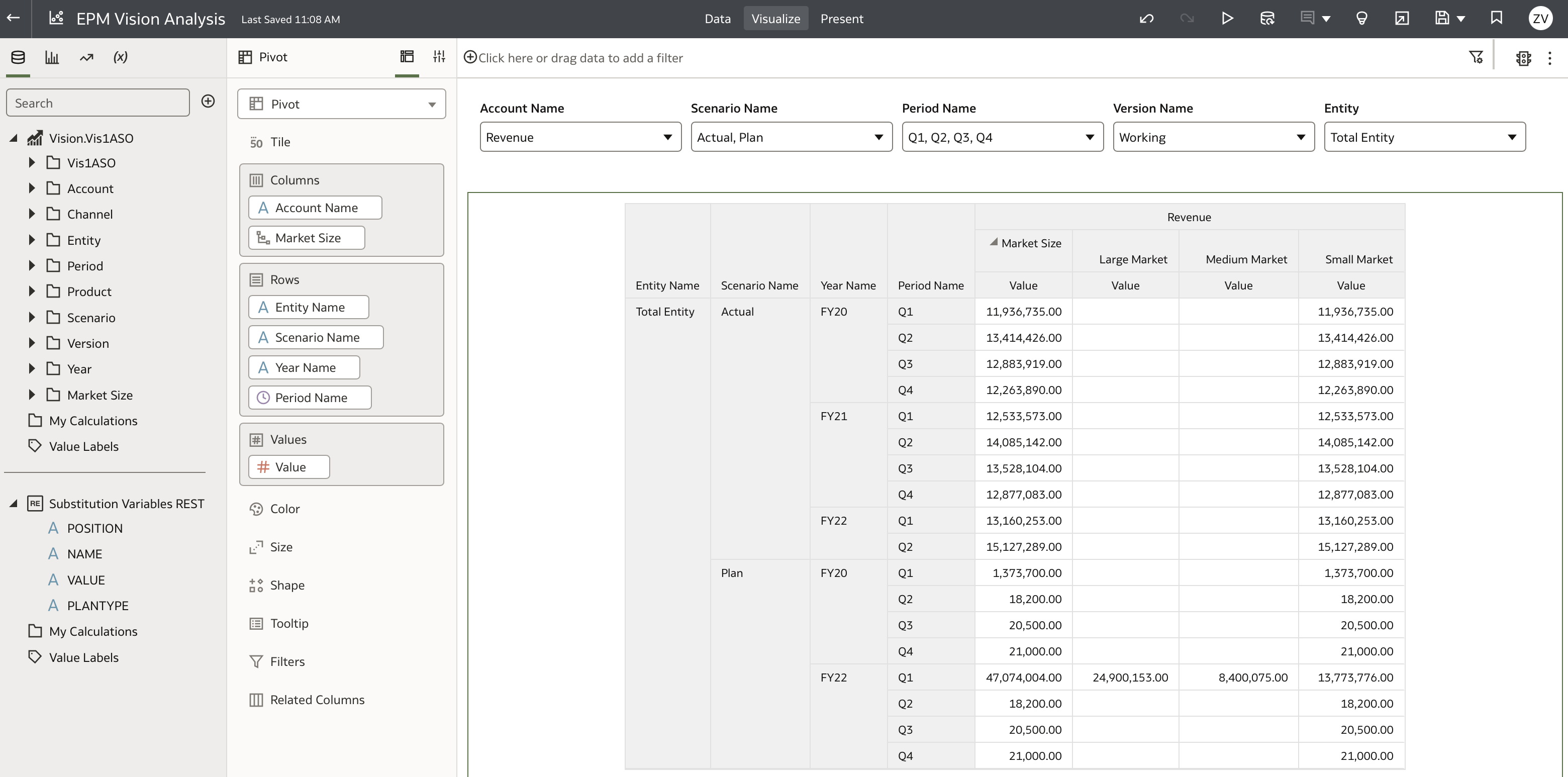
The Vision.Vis1ASO dataset connects through an EPM direct connection, which allows access to five plan types or cubes. In this example, we use the Vis1ASO plan type.

The EPM direct connection is configured as shown below:
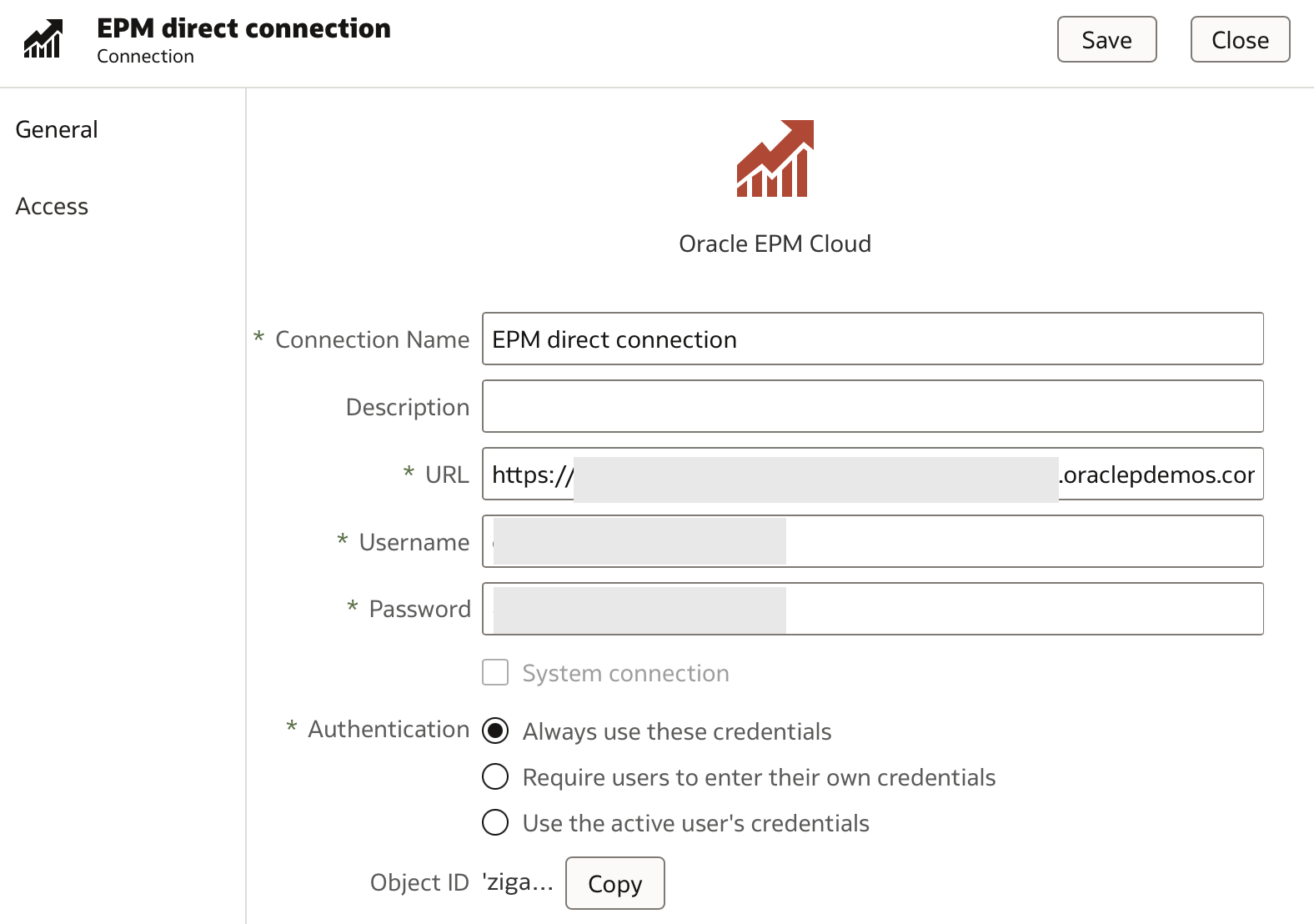
The URL corresponds to the base URL of the EPM Cloud Service. For example, if the service URL is https://xxx-xxx-xxx.eu-frankfurt-1.ocs.oraclecloud.com/epmcloud, then the required URL is https://xxx-xxx-xxx.eu-frankfurt-1.ocs.oraclecloud.com.
Oracle's EPM connector supports three authentication options:
- Always use the credentials defined in the connection.
- Require users to enter their own credentials each time they use the connection.
- Use active user credentials, where the credentials used to connect to Oracle Analytics are automatically used for EPM Cloud.
Creating a REST API Connection to Retrieve Substitution Variables
To access substitution variables, we need to create a new connection using the Oracle EPM Cloud REST API.
Oracle's documentation comprehensively covers how to work with the EPM Cloud REST API; more details can be found here.
Start by clicking Create and selecting Connection:
In the Create Connection window, scroll down to find REST API (Preview) and select it:

Name your connection (e.g., EPM REST API Connection), then specify the REST base URL.
When working with Oracle EPM Planning as a data source, the REST API URL syntax is:
https://<BASE-URL>/HyperionPlanning/rest/{api_version}/{path}
Where:
- BASE-URL is the first part of your EPM service URL. For example, if your service URL is
https://xxx-xxx-xxx.eu-frankfurt-1.ocs.oraclecloud.com/epmcloud, then BASE-URL ishttps://xxx-xxx-xxx.eu-frankfurt-1.ocs.oraclecloud.com. - api_version is the REST API version, currently v3 for Planning.
- path identifies the resource. For substitution variables, the path is
/HyperionPlanning/rest/{api_version}/applications/{application}/substitutionvariables. For example, using the planning application Vision.
Assuming an instance with the following BASE-URL:
https://epm-1234567890-plan.demoservices.oraclepdemos.com
The full REST Endpoint URL becomes:
https://epm-1234567890-plan.demoservices.oraclepdemos.com/HyperionPlanning/rest/v3/applications/Vision/substitutionvariables
Add this endpoint by clicking Add Endpoint and replacing the suggested URL with the one above.
For Authentication, select Basic and enter your username and password.
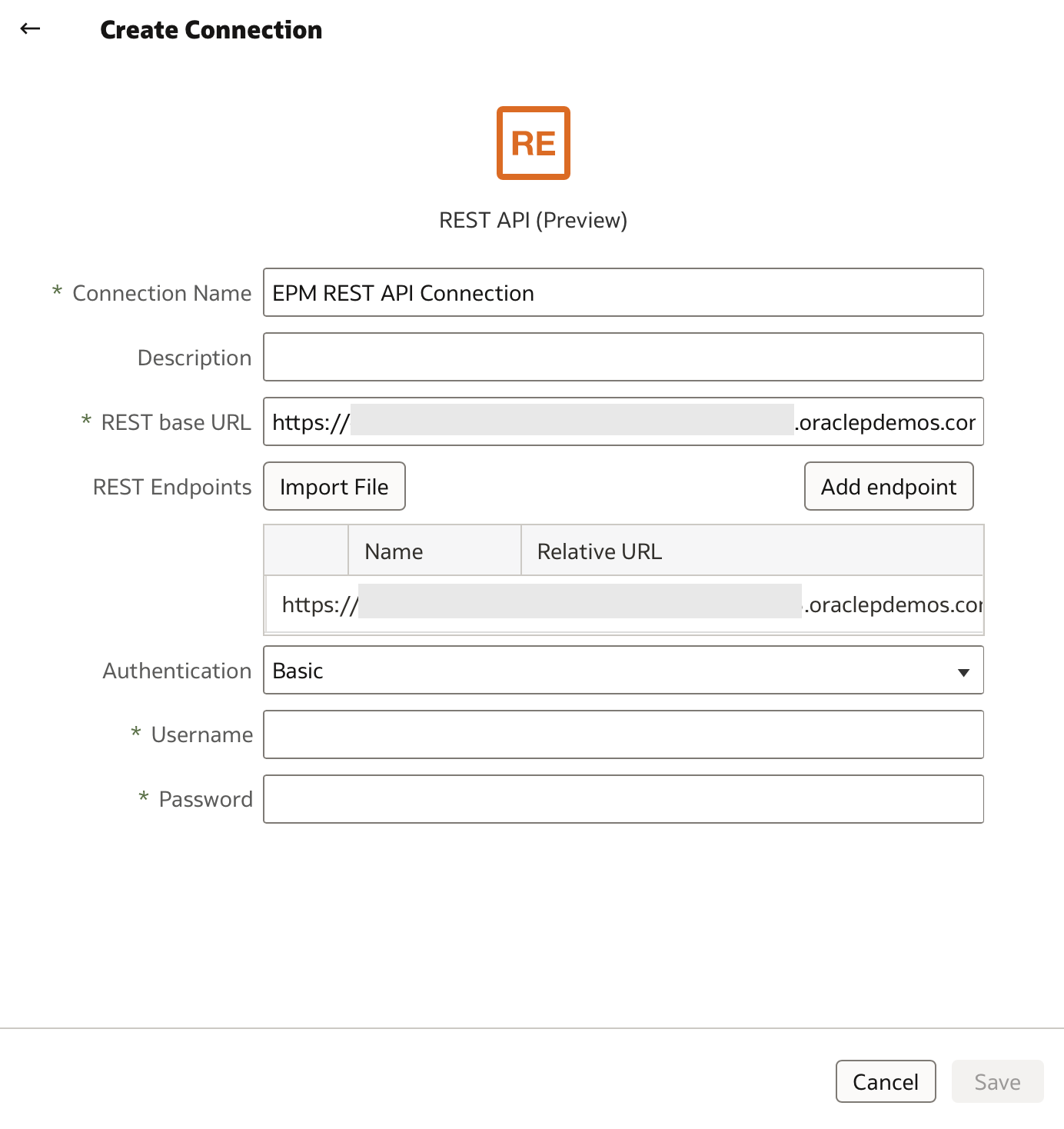
Click Save. If successful, a confirmation message will briefly appear.
Creating a Dataset to Capture Substitution Variables
Next, create a dataset that retrieves substitution variables using the REST API connection.
From the list of available connections, select the one you just created. Open the Actions menu on the right and choose Create Dataset:
In the New Dataset page, expand Schemas on the left panel, then open AUTOREST:
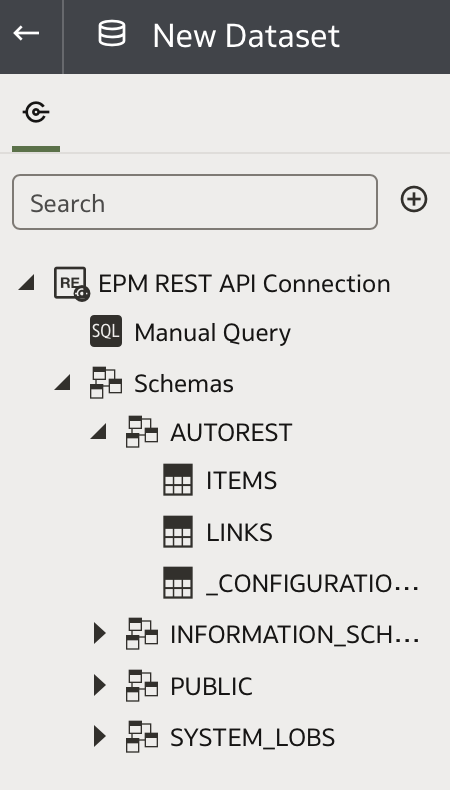
Double-click or drag the ITEM object onto the canvas.
This action retrieves all substitution variables from the Oracle EPM Planning application (Vision) via the REST API.
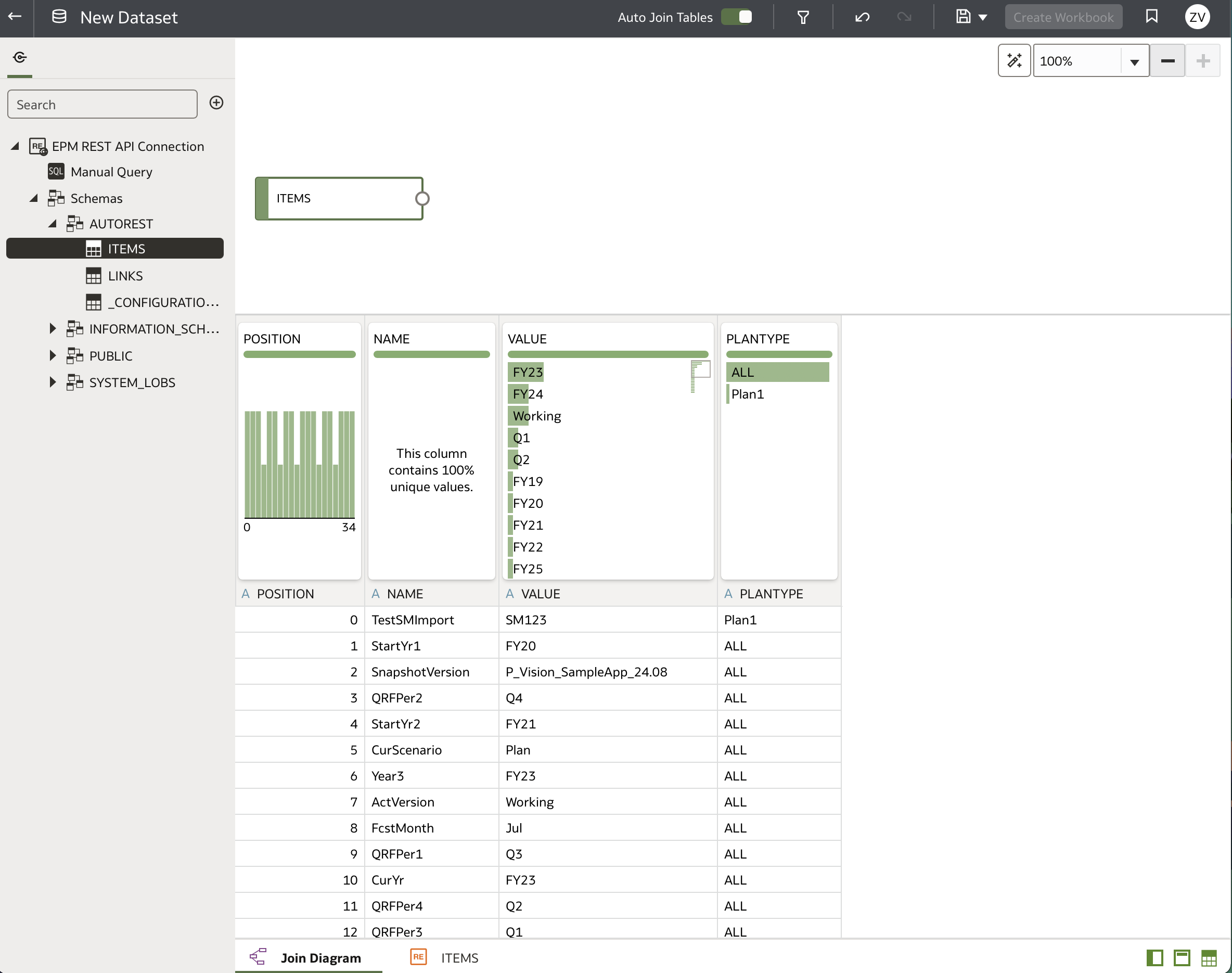
The dataset contains four columns:
- POSITION: Substitution Variable ID
- NAME: Substitution Variable name (e.g., ActVersion)
- VALUE: Substitution Variable value (e.g., Working)
- PLANTYPE: Plan type or cube associated with the substitution variable
Name and save your dataset appropriately.
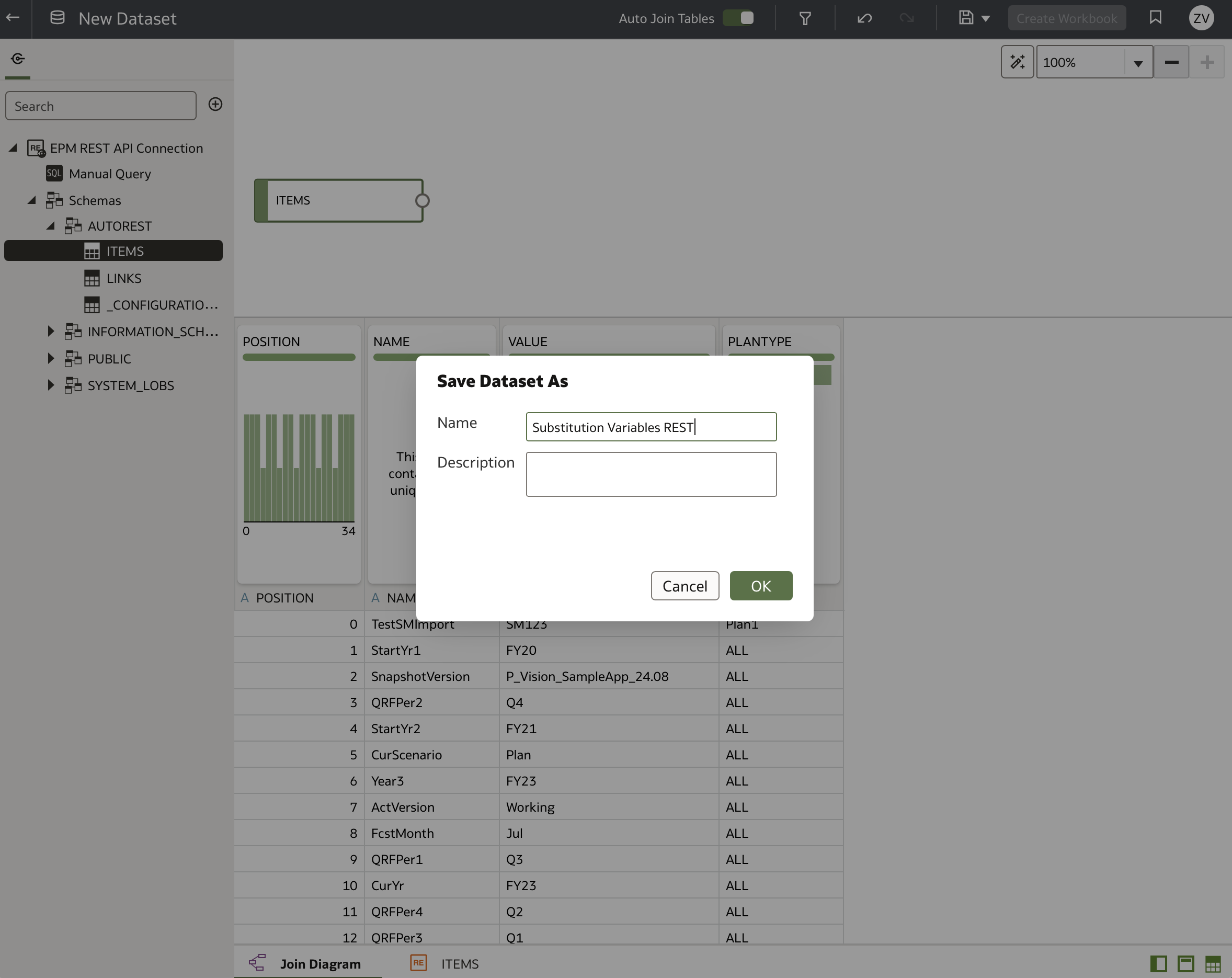
Now, this dataset can be used like any other dataset in Oracle Analytics Cloud.
Integrating Substitution Variables into Analyses
Return to the initial workbook based on the Vision Planning application:
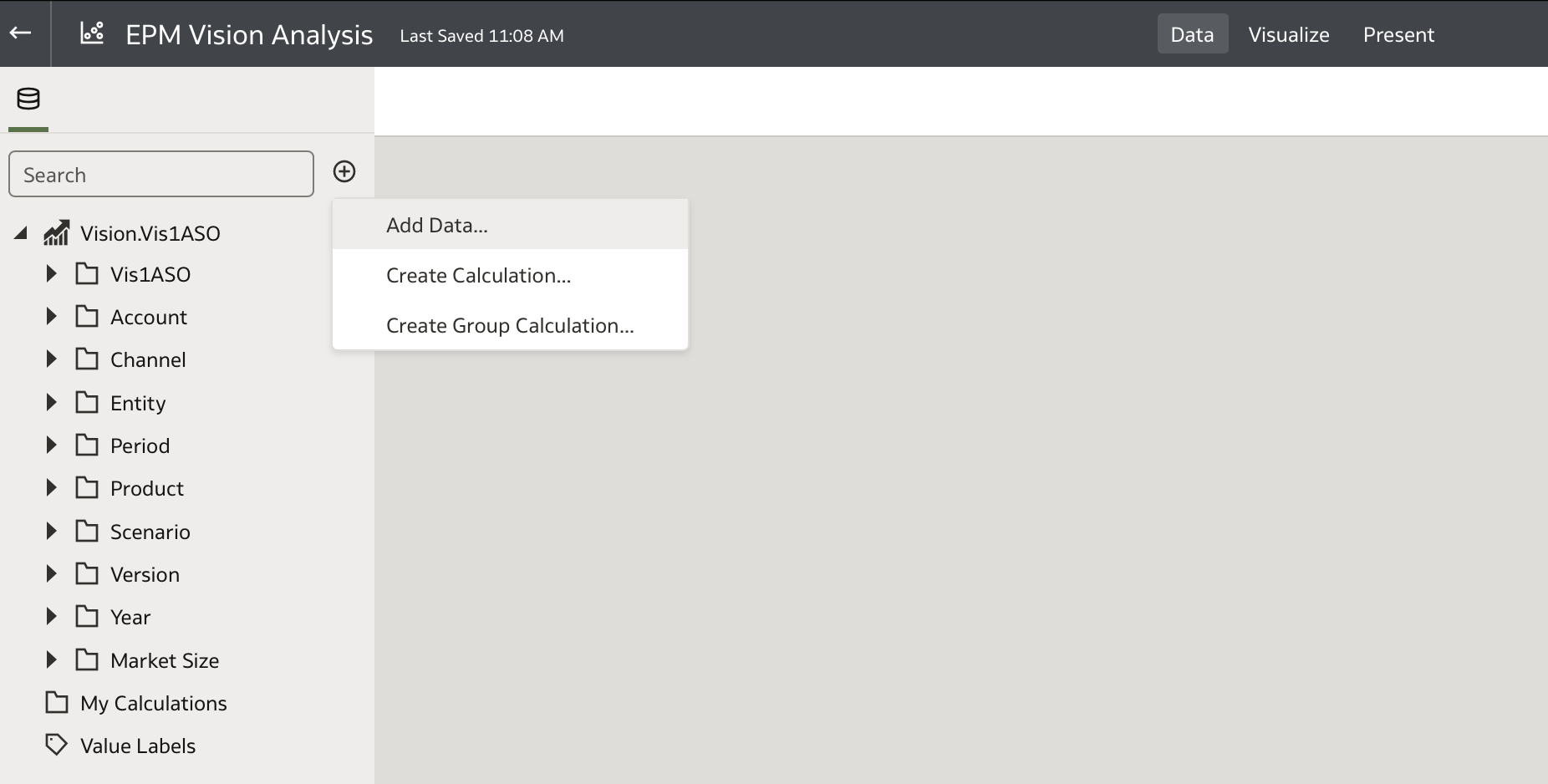
Since the direct EPM Connector does not retrieve substitution variables, add the REST API dataset created above as an additional data source.
Go to the Data tab and click Add Data ...:
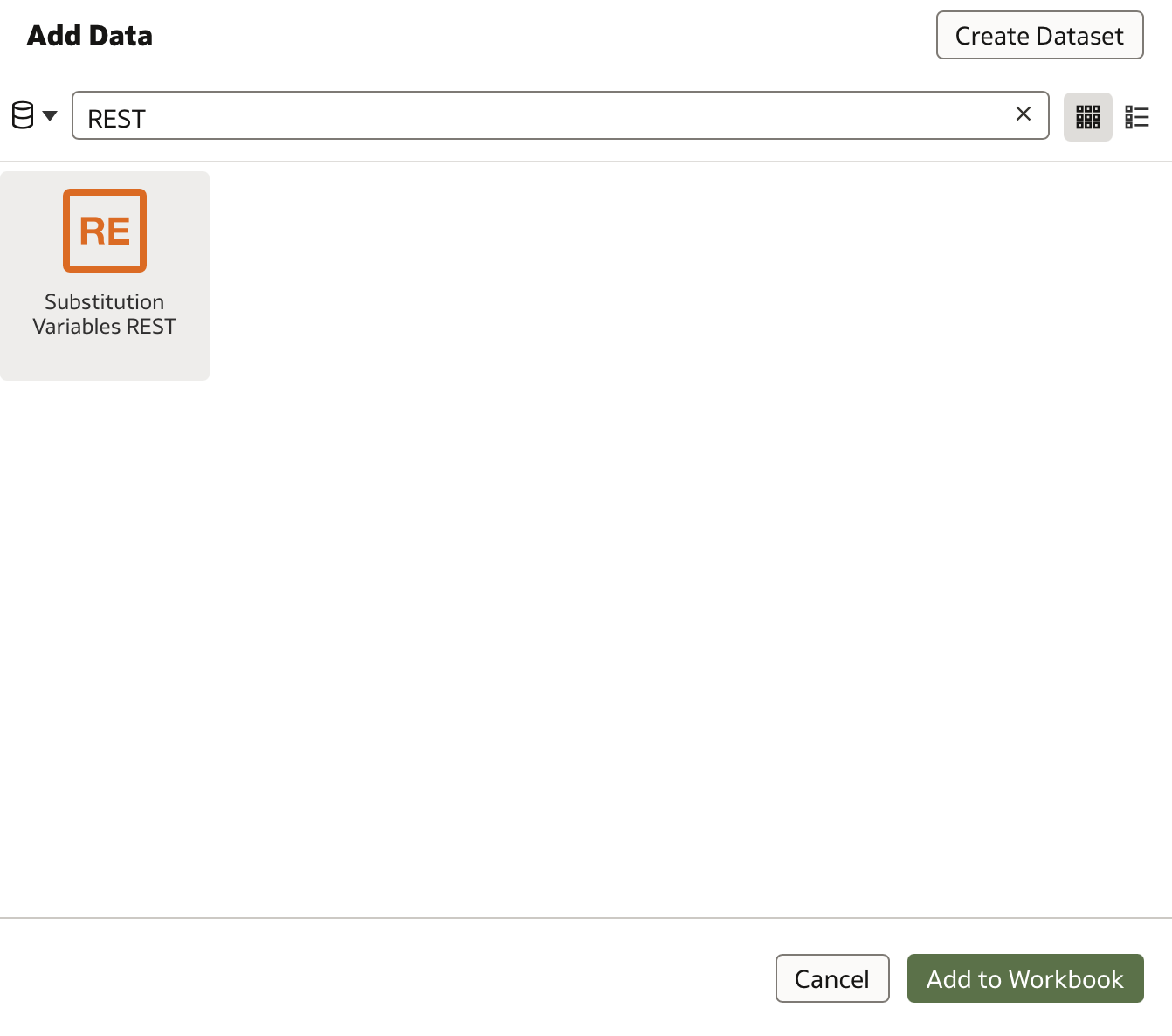
Search for your REST API dataset and click Add to Workbook:
The Substitution Variables REST dataset will now appear in the datasets list on the left panel:
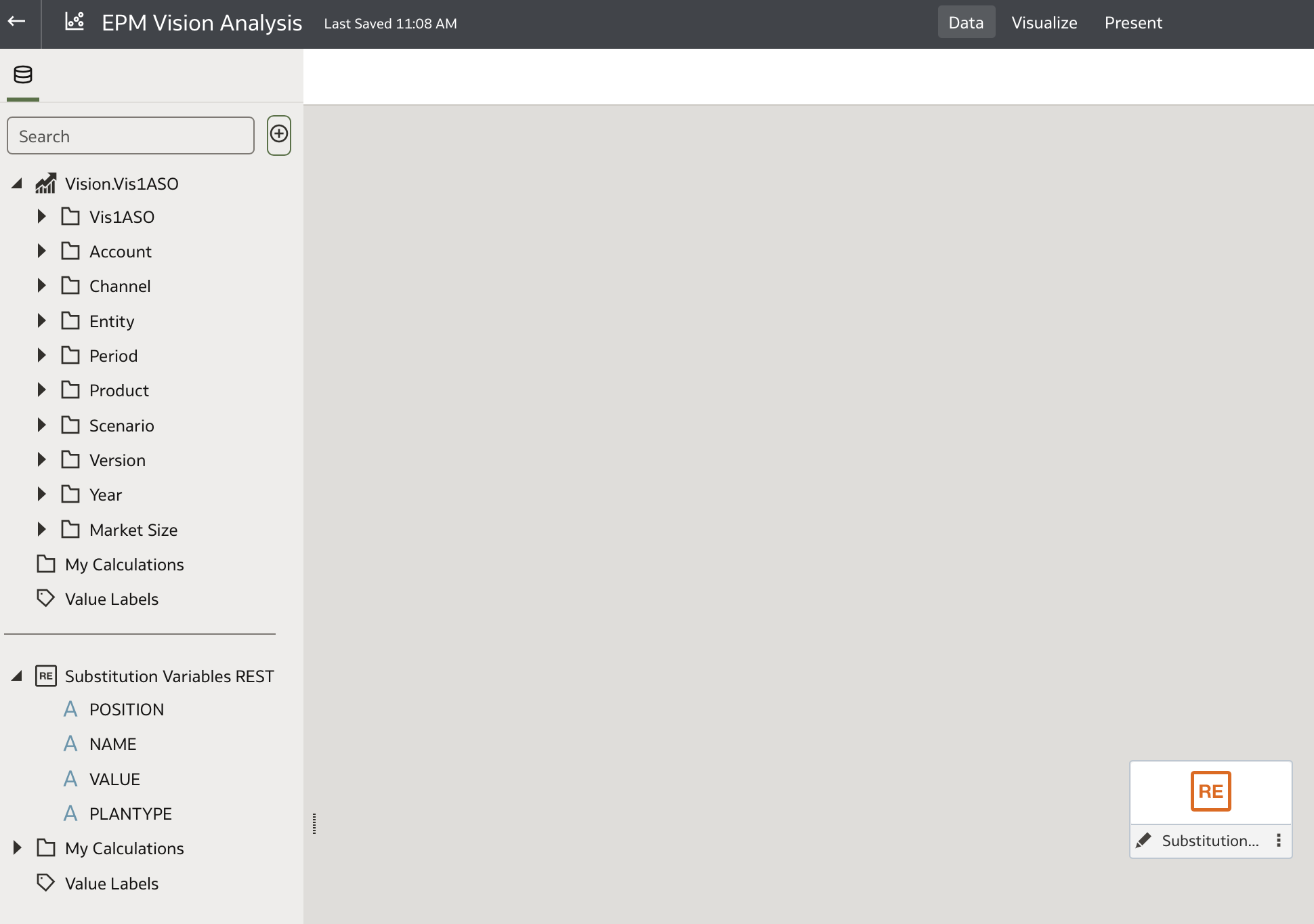
This dataset is independent of the Vision data and does not require any relationships. Its purpose is to populate parameters for filtering or other uses.
Switch back to the Visualize tab.
Using Substitution Variables for Filtering
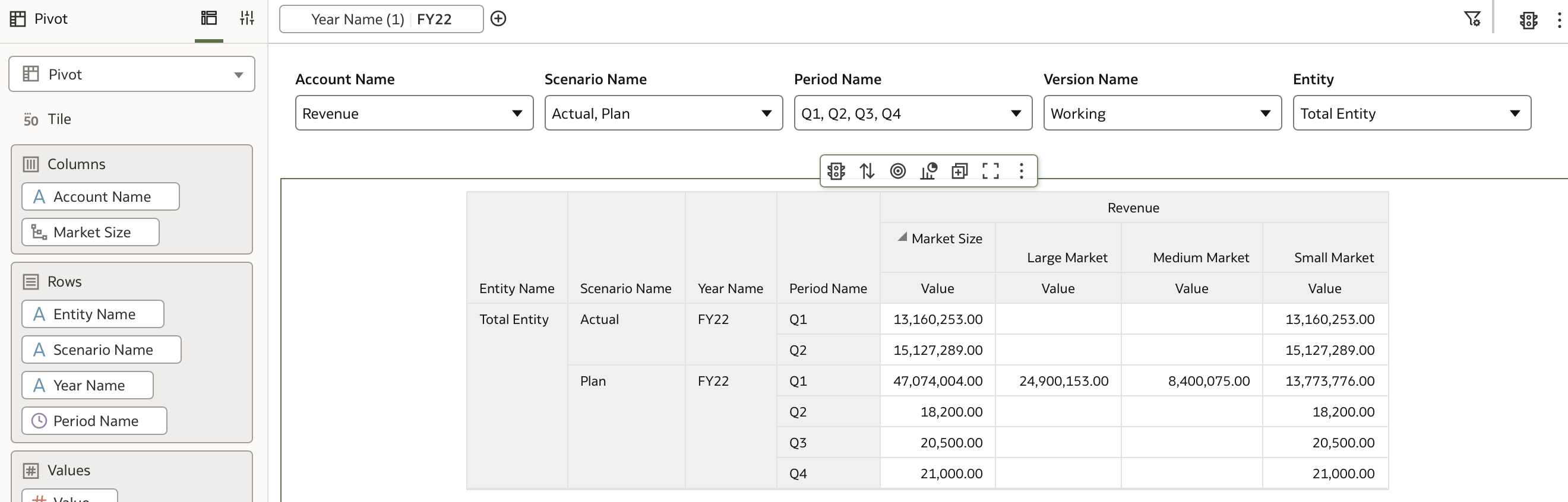
A common use case is to filter data based on substitution variable values. For example, we will populate a parameter called Year Parameter with the value of the LastYr substitution variable, which in this case is FY22.
First, review all substitution variables:
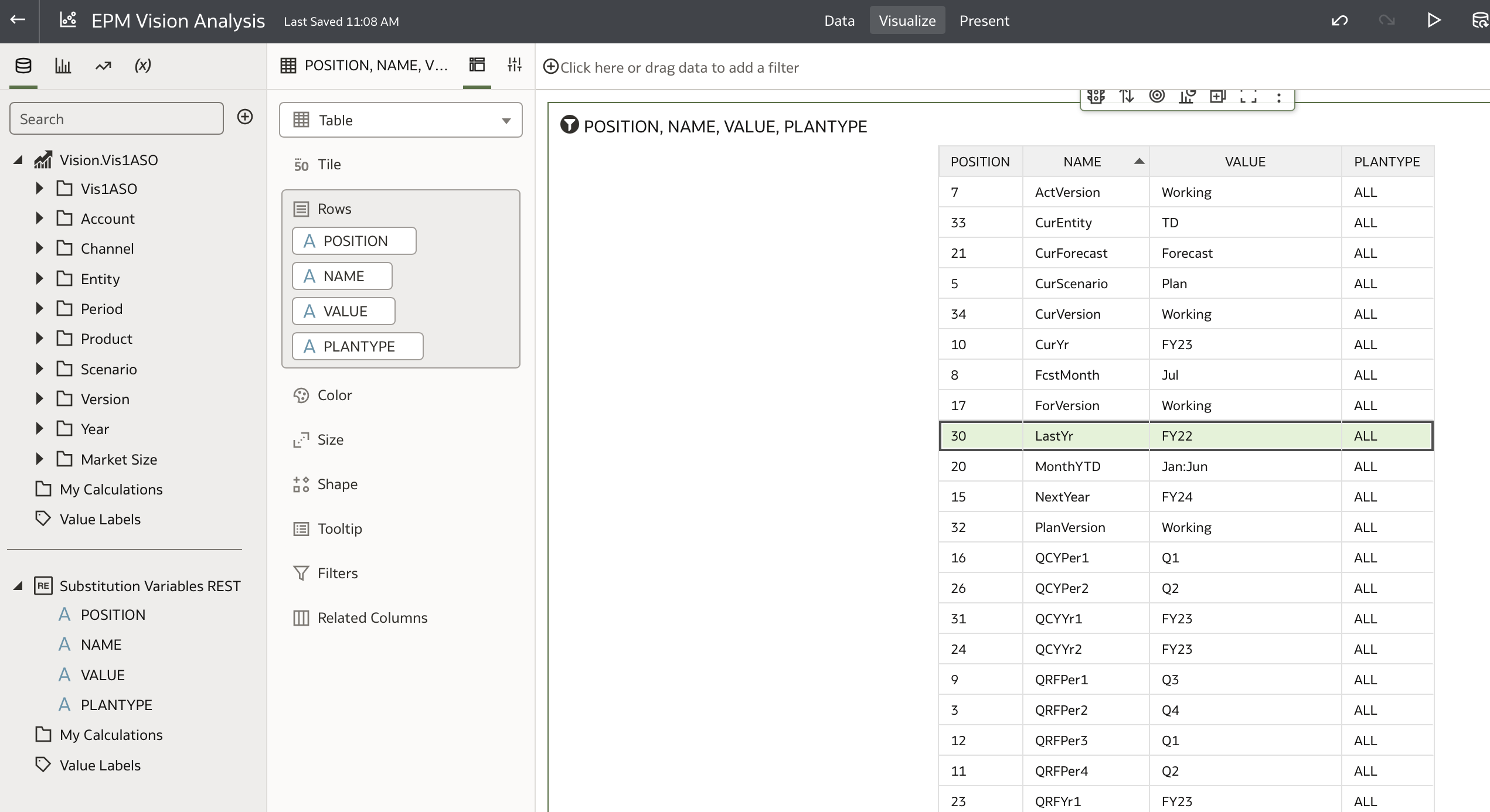
Confirm that LastYr has the value FY22.
Navigate to the initial analysis and create a new filter on the Year Name column:
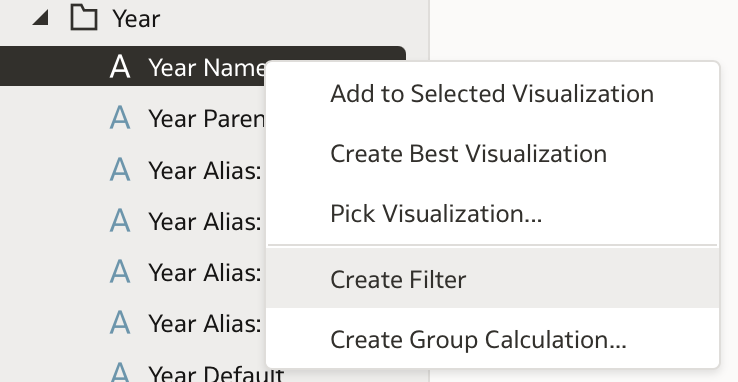
Instead of selecting values manually, click the (x) Bind Parameter icon:
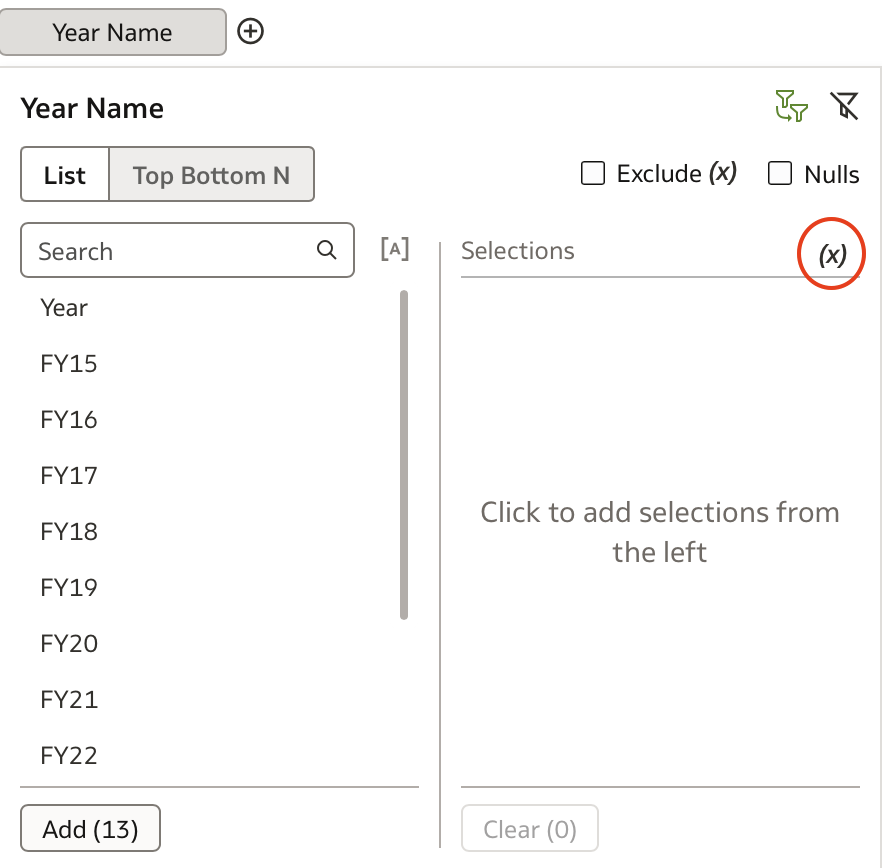
From the menu, choose Create Parameter:
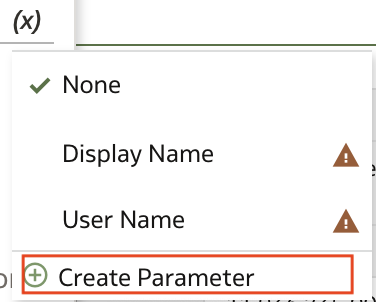
A new parameter is created with a temporary name Year Name.
Right-click the parameter and select Edit Parameter to configure it.
Rename it to Year Parameter and set Allow Multi Select to off. Change the Initial value setting to Logical SQL Query.
Use the following Logical SQL query (you can generate this by creating a visualization and using the Developer option to extract the Logical SQL):
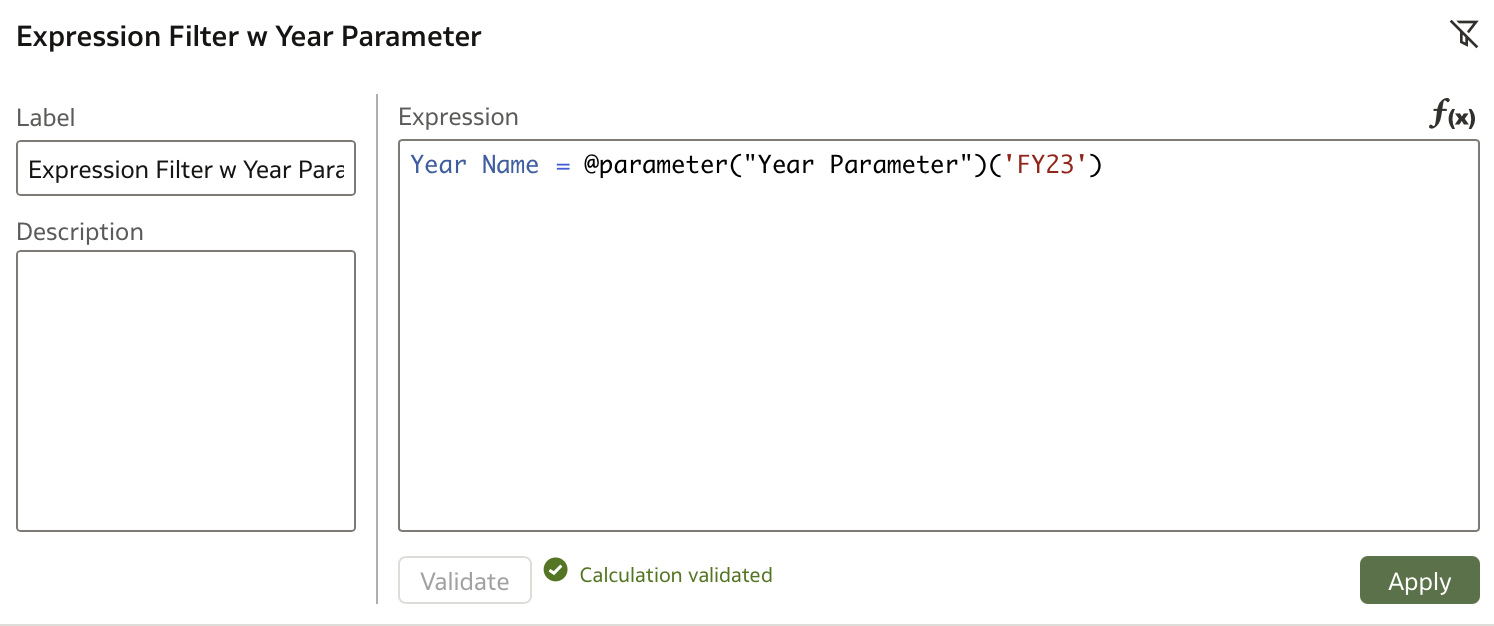
SELECT XSA('ziga.vaupot@version1.com'.'Substitution Variables REST')."ITEMS"."VALUE"
FROM XSA('ziga.vaupot@version1.com'.'Substitution Variables REST')
WHERE XSA('ziga.vaupot@version1.com'.'Substitution Variables REST')."ITEMS"."NAME" = 'LastYr'
Binding this parameter to the filter applies the filter based on the substitution variable's predefined value:
Moreover, the parameter can be used independently. For example, disable the workbook filter and instead apply an Expression Filter using the parameter:
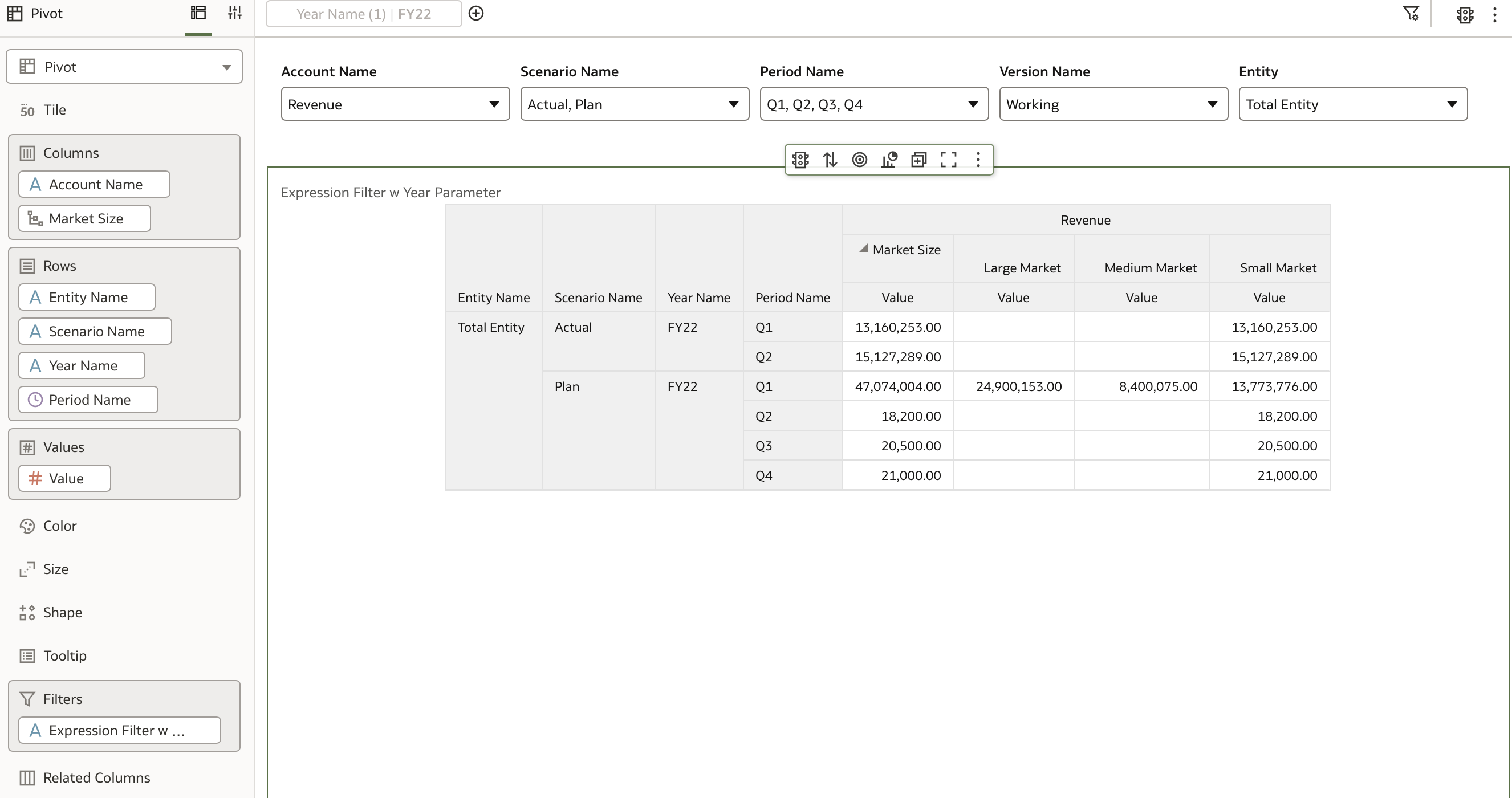
The result is the same filtered data:
Conclusion
This exercise demonstrates how Oracle EPM Cloud can be integrated as a data source in Oracle Analytics. While the direct connection supports data retrieval, substitution variables require leveraging the REST API.
Looking ahead, Oracle has announced that Oracle EPM Cloud and Essbase will be supported as data sources in the Semantic Modeler starting with the January 2025 release. This enhancement is expected to simplify the retrieval of substitution variables directly within the Semantic Modeler, eliminating the need for separate REST API connections.
Another eagerly anticipated feature is Selection Steps, which will allow users to filter and display specific sub-hierarchies within dimensions (e.g., selecting just the P&L or Balance Sheet within the Account dimension). Currently, hierarchical columns display all members, and while some can be manually removed, upper levels remain visible, limiting usability. Selection Steps are planned for the March 2025 release.
Together, these upcoming capabilities promise to significantly enhance Oracle Analytics' integration with Oracle EPM Cloud and Essbase, improving user experience and analytical flexibility.
Wishing you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year 2025!