Let’s assume you already have a deployed semantic model in your Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) environment. Now, you want to enable collaboration by allowing multiple developers to work on this model simultaneously.
In the past, OBIEE supported collaboration through the Multi-User Development Environment (MUDE). However, MUDE had its challenges—locking conflicts, merge complexities, and deployment issues were common pitfalls.
With the introduction of Semantic Modeler in Oracle Analytics, collaborative development is more robust and streamlined. Developers can either:
- assign permissions within Semantic Modeler, effectively making it a built-in multi-user environment, or
- integrate with Git, which brings version control and true collaborative development via source control access rights.
In this article, we’ll walk through how to integrate Semantic Modeler with Git for the first time.
Integrating Semantic Modeler with Git is relatively straight forward process that can be accomplished within a few steps. Each Semantic Modeler in the list of models has associated menu (accessible on the right hand side).
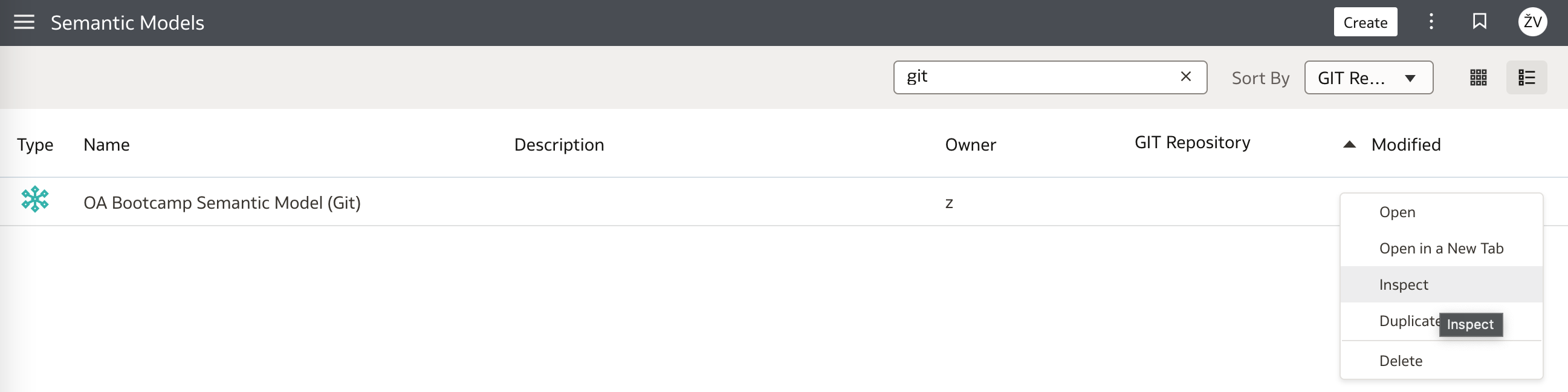
Selecting Inspect menu option opens a window in which users decide and set their development environments - under Sharing tab on the left side menu:
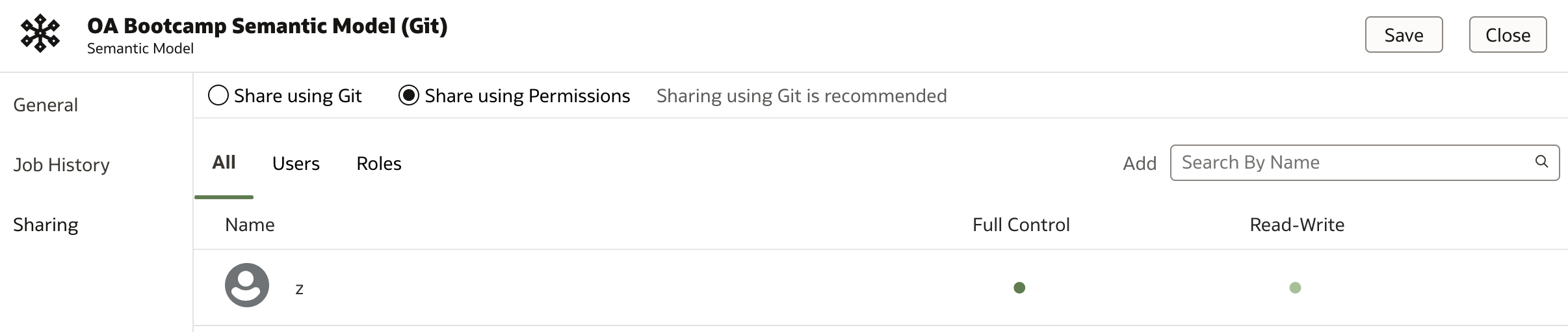
Permissions
Git
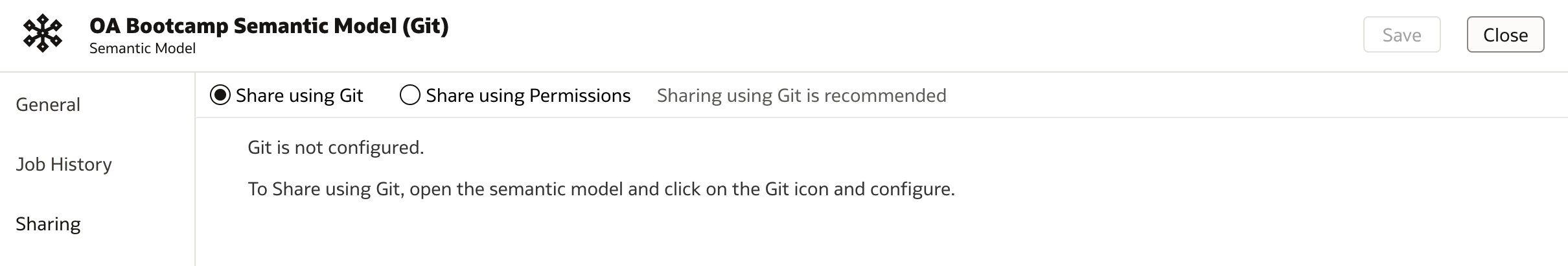
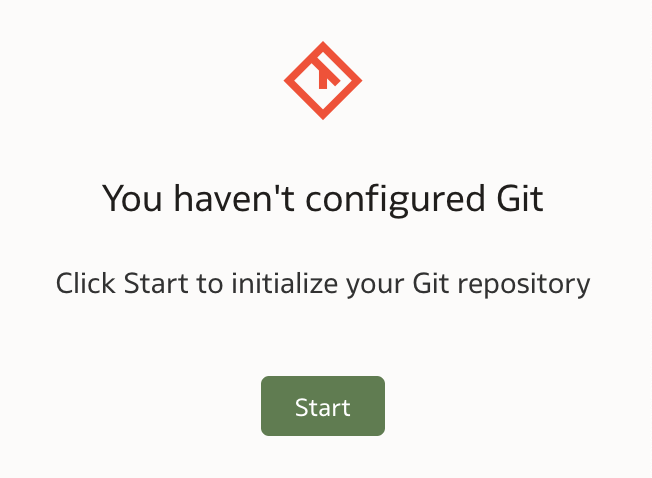
As you can see, Git is by default preferred option. However in my case it hasn't been configured yet. To configure git integration, one must open Semantic Model and click Git icon (located in bottom-right corner).
Because this is my first attempt to configure Git, it has to be initialized first.

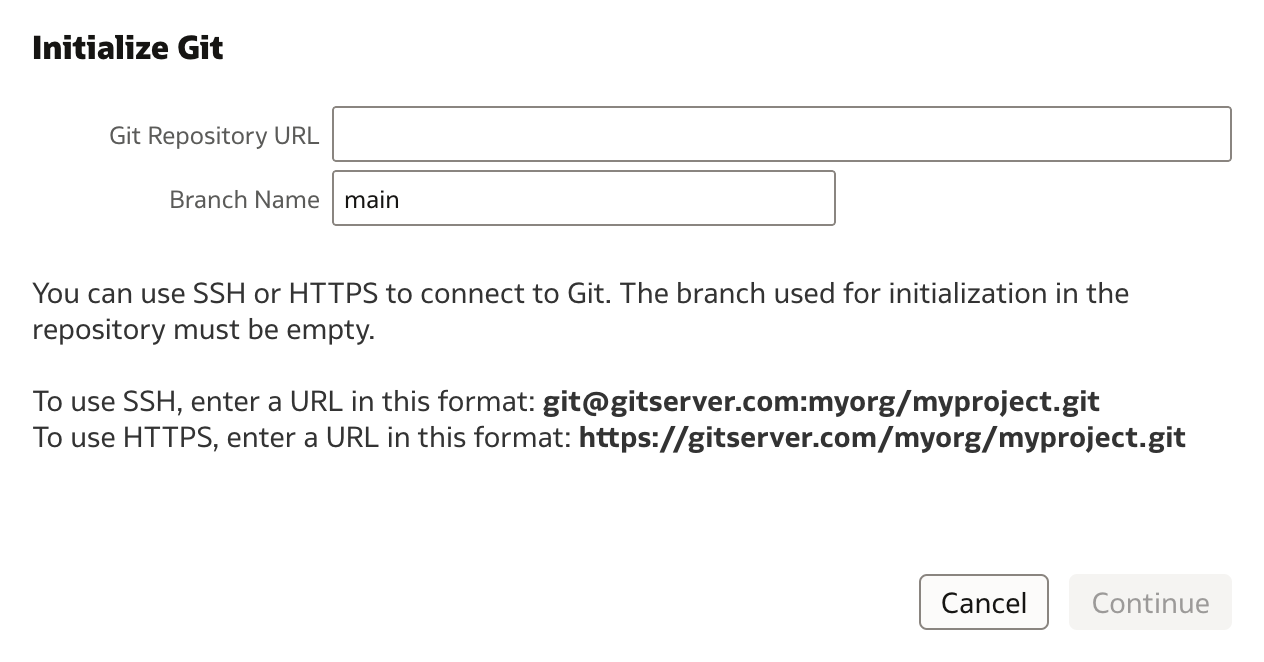
Initialize Git window opens. It is assumed that Git repository has already been created, so Git repository URL should be provided.
Just for the further reference, here is my Git repository for this case:
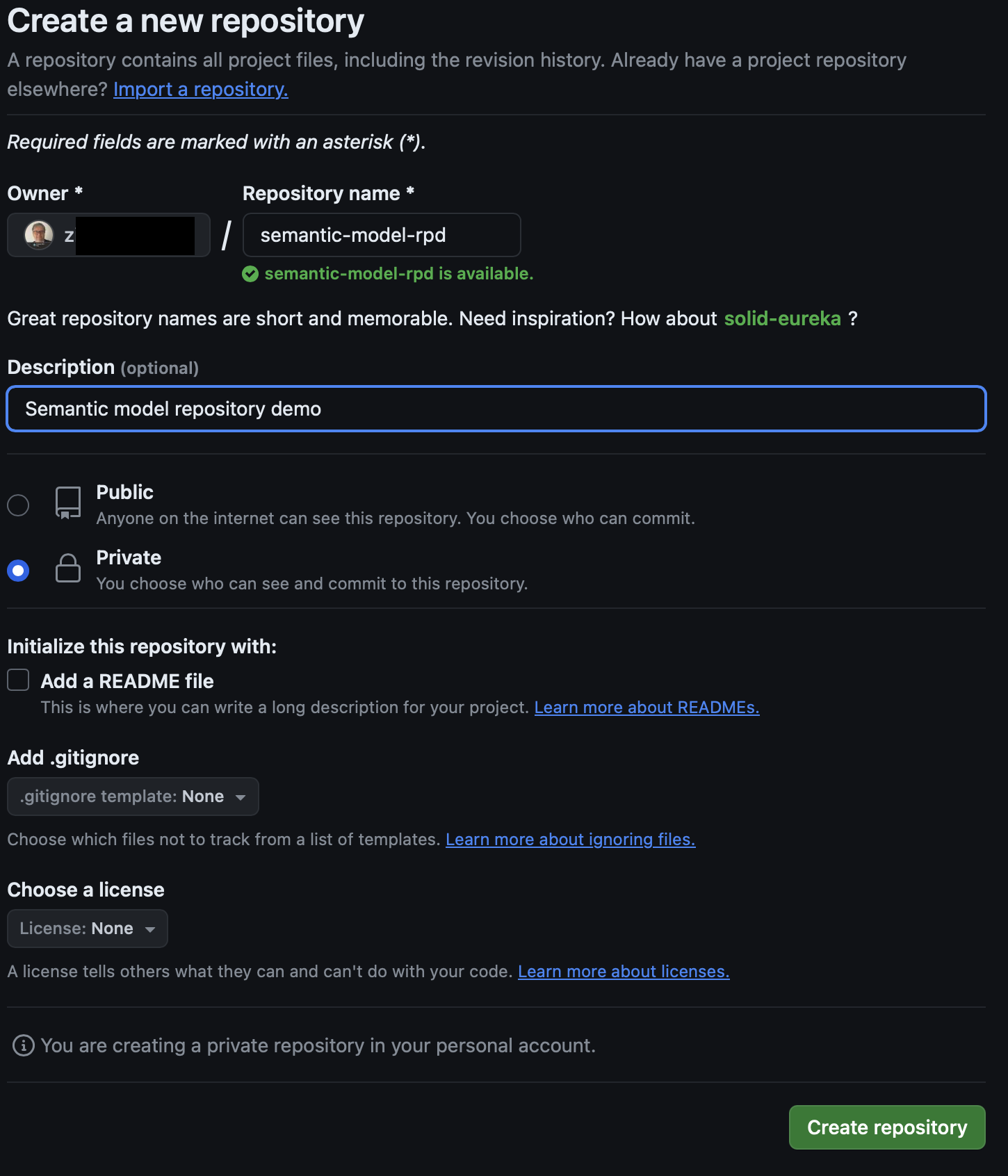
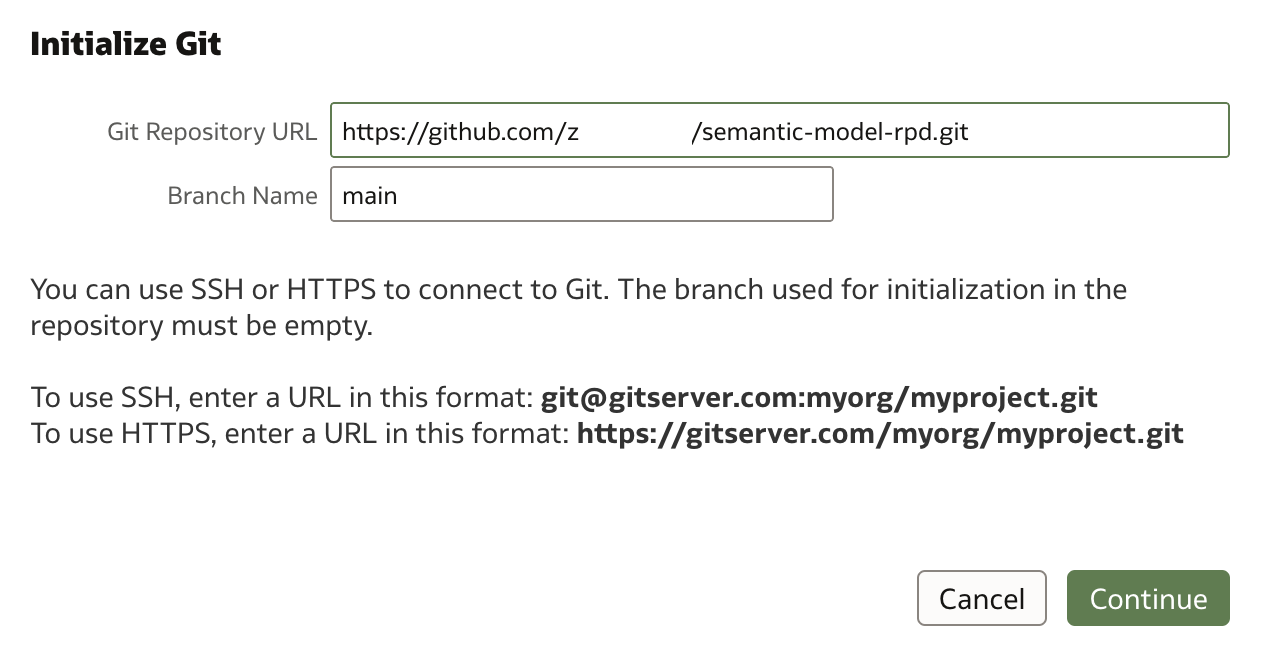
As it is also shown in instructions, there are two options for providing required URL, HTTPS or SSH. In my example, I am using HTTPS, but either of two URLs can be used:


Once URL has been copied into Git Repository URL and Branch Name provided, i.e. main (assuming this is main branch), setup can continue.
In the next step, you’ll need to define a Git user profile. Along with the username, Git also requires a password. Note that this isn’t your Git login password, but rather a Personal Access Token, which you generate from your Git account.
Here are the steps to generate Personal Access Token:
In Git, navigate to user's Settings and then to Developer Settings. Open Personal access tokens and then click on Fine-grained tokens.
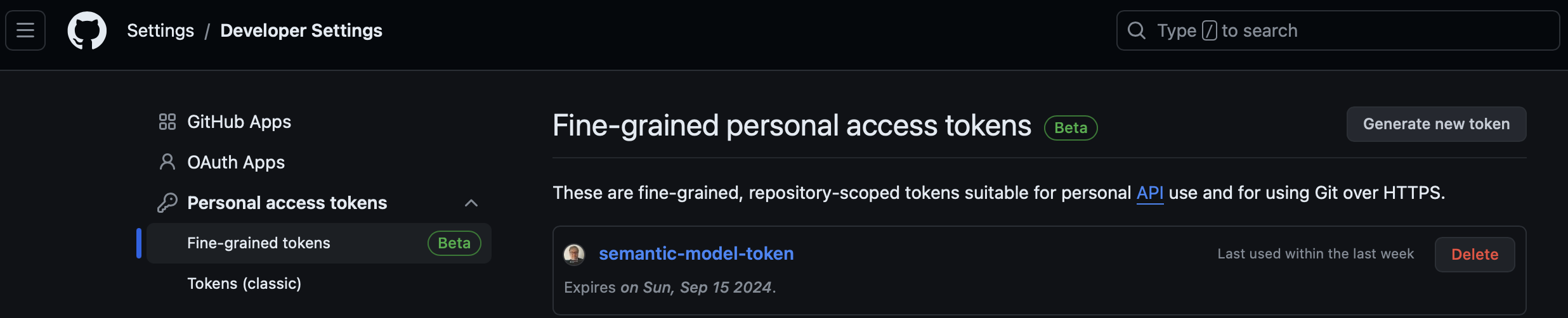
Click Generate new token.
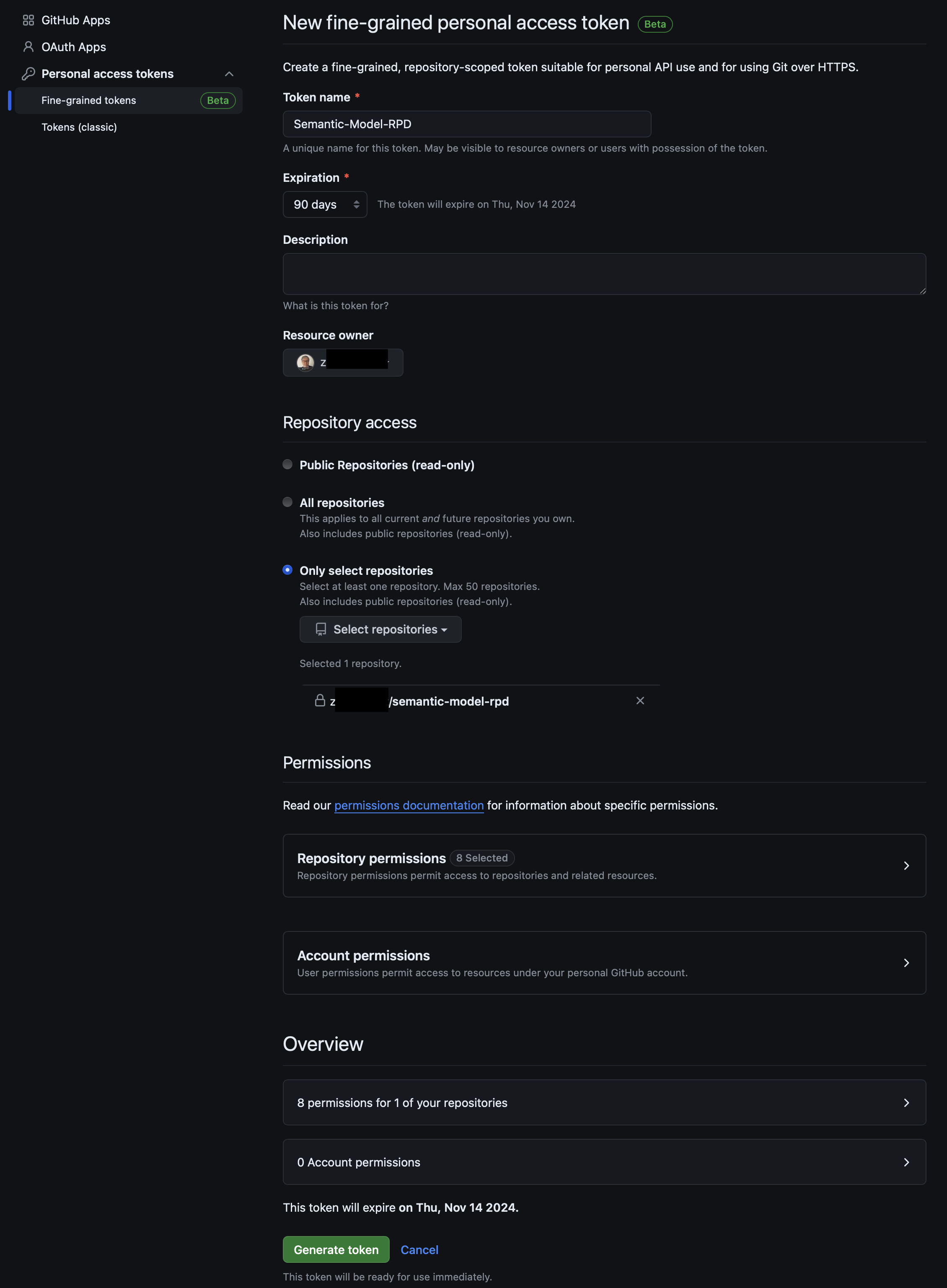
Provide a new token name, set expiration date, optionally define for which repository is this token valid, and then click Generate token.
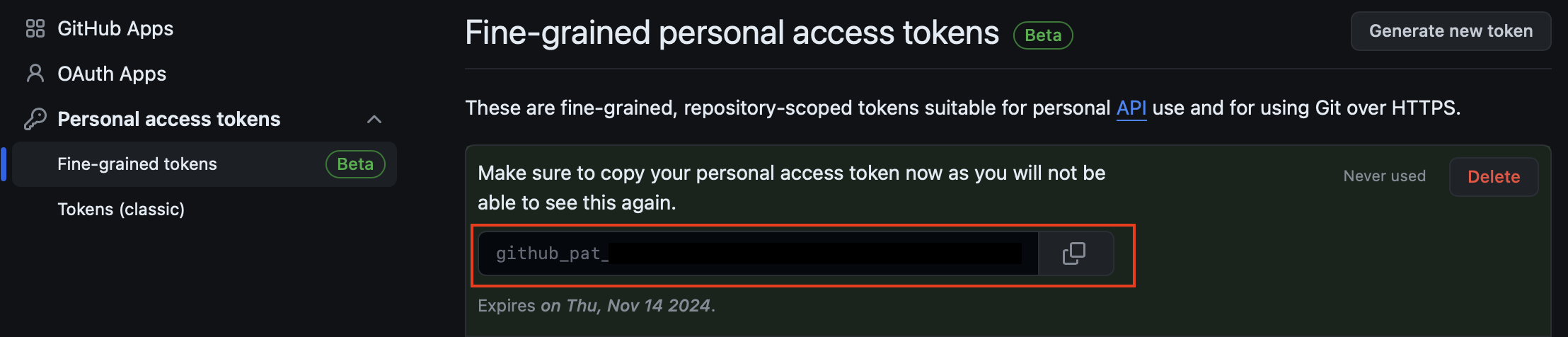
When token is generated, copy it into clipboard. Use this token and fill the password field in Initialize Git popup window.
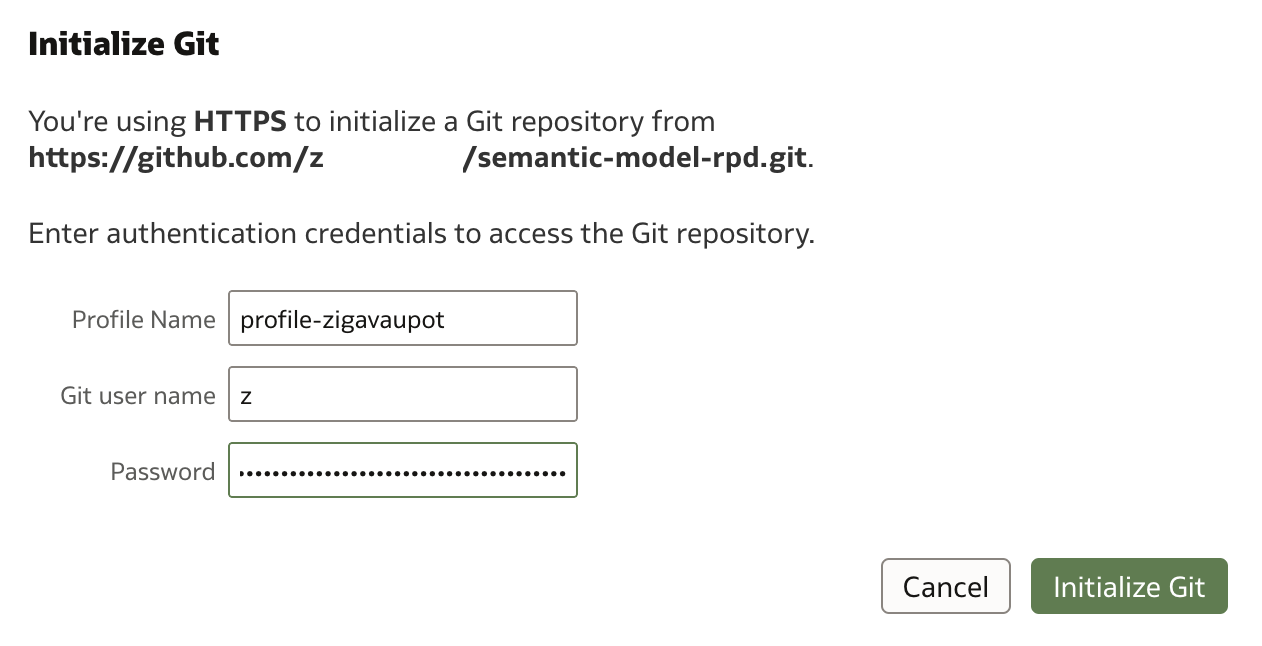
After a couple of seconds, Git is initialized.

The results of Git initialization can be now reviewed in you Git environment, Github in my case:
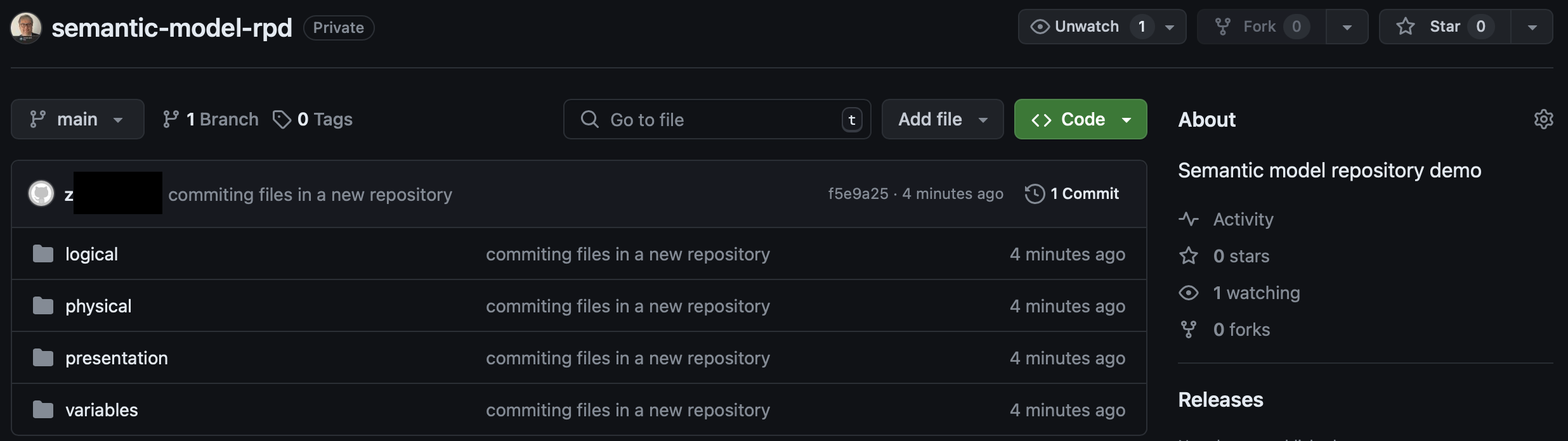
As you can see there are four folders created which replicate Semantic Modeler content:
- three folders for each layer of semantic model: physical, logical and presentation,
- additional folder for variables.
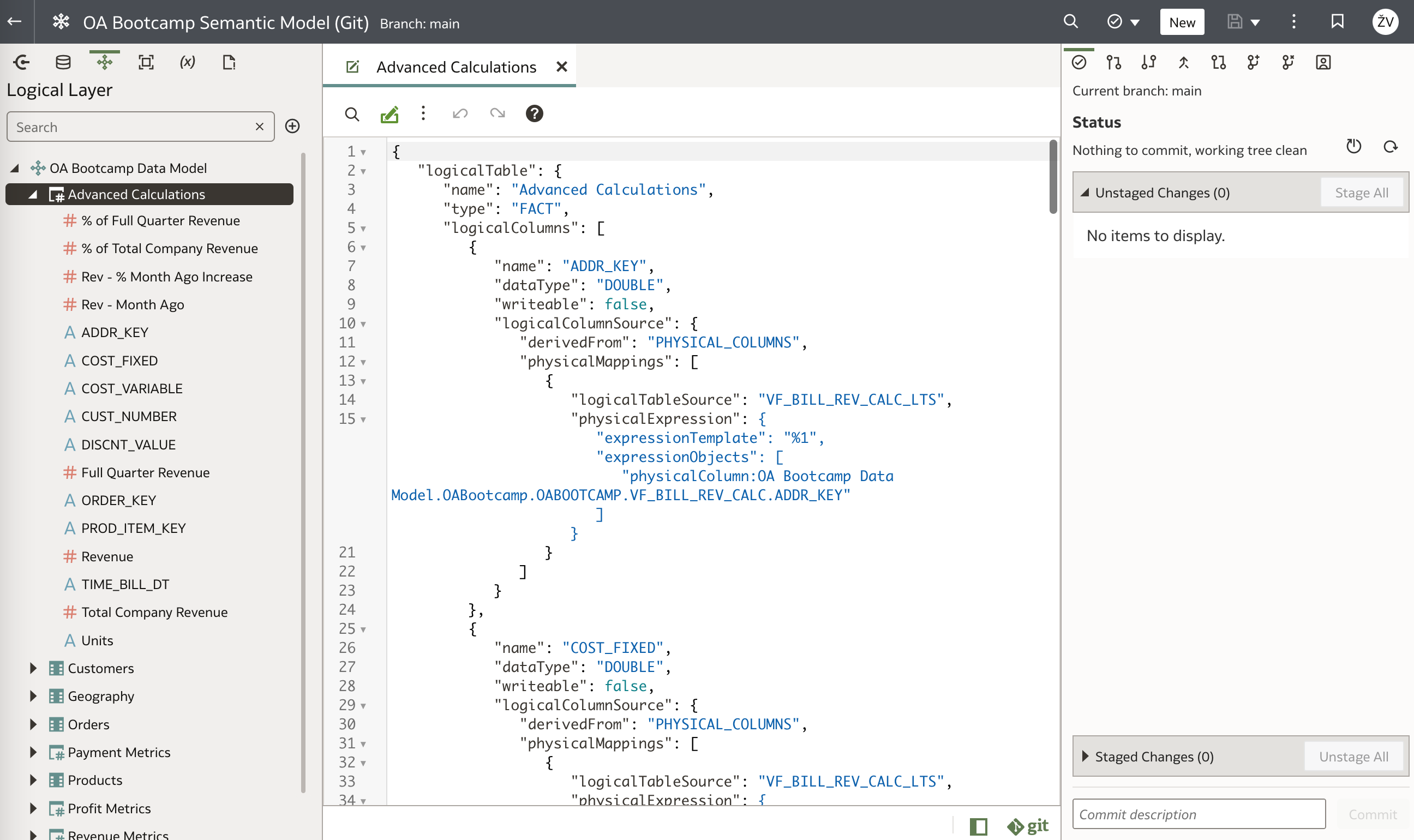
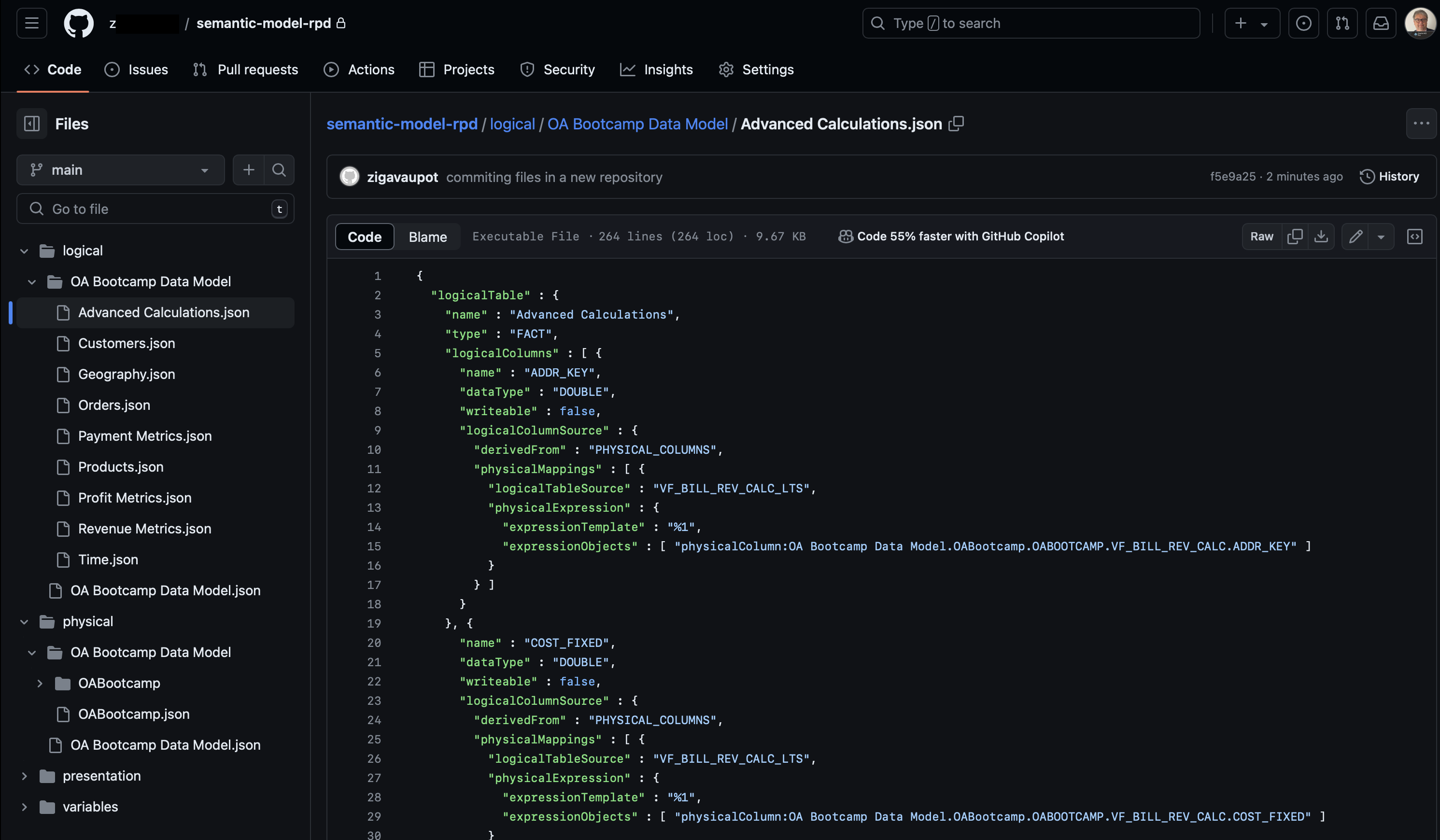
Drilling down the folder structures shows semantic model structure and its definitions in SMML (JSON). When comparing with Semantic Model that resides in OAC, we can see that the content is exactly the same.
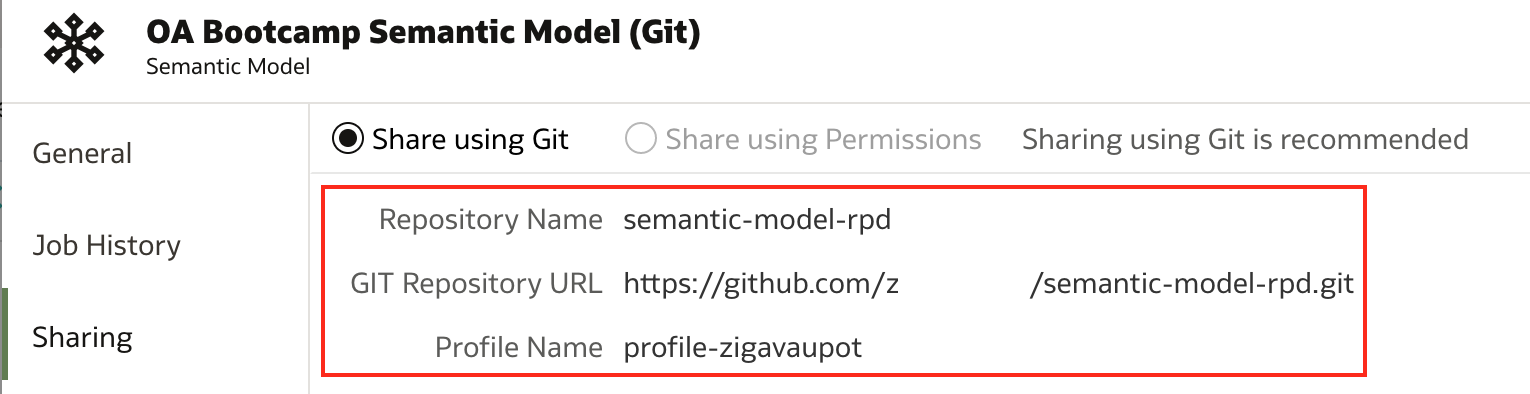
There is also one minor detailed available for inspection in Oracle Analytics' Semantic Models list - for the model that we initialised Git repository, connection to the Git repository is now displayed:
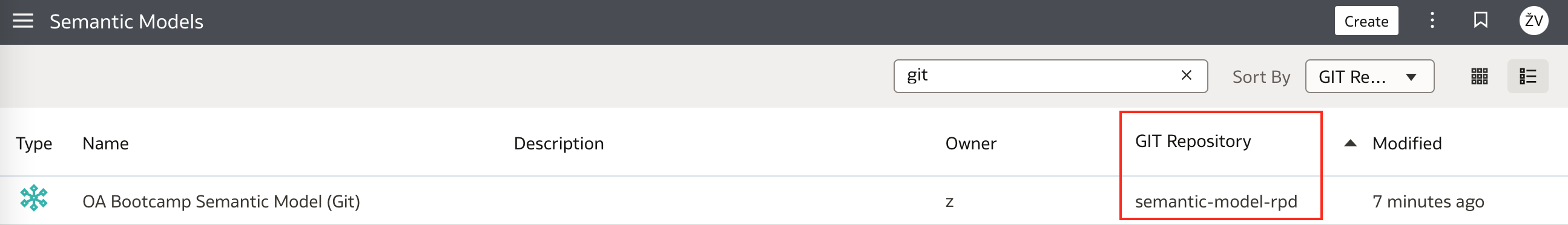
And detailed description of connection is available as well:
Final Thoughts
This walkthrough demonstrated how to connect Semantic Modeler with a Git repository. In upcoming posts, we’ll explore real-world use cases of this integration, including:
- migrating semantic models between environments,
- multi-user development environment,
- model versioning.